Occupational skin diseases are the second-most common type of occupational disease. NIOSH estimates that more workers are potentially exposed to chemicals that can be absorbed through their skin. Workers at risk of occupational skin diseases include those in construction, health care, agriculture, food service, auto repair and cosmetology. Occupational skin diseases are skin diseases caused by exposure to hazardous agents or substances present at workplace.
Examples of occupational skin diseases are: (Refer table)
| Occupational Skin Diseases |
Features |
Common Hazardous Agent |
| Occupational contact dermatitis |
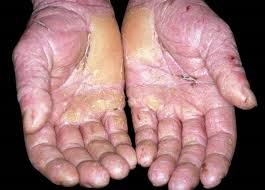
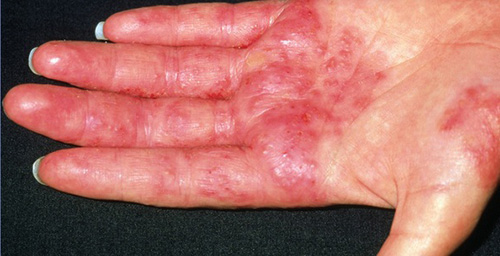
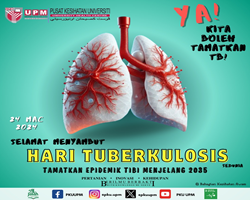
- Skin becomes red with painful, multiple small-watery-round shape swelling following contact or exposure to certain agent at workplace.
- Usually at site of contact but may spread to other sites as well.
|
Dyes, rubber, formaldehyde, flour, pesticide, formaldehyde, solvents, cement, detergent, diesel, paraffin, thinner |
| Occupational skin cancer |
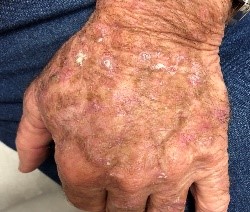
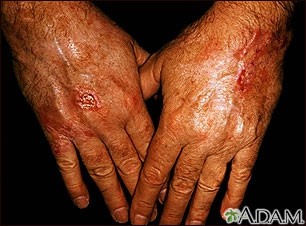
- Cancer develops following continuous exposure to certain agent at workplace.
- Skin becomes red, scaly with swelling and ulcerated.
|
Ultraviolet light exposure, ionising radiation, soot, tar, mineral oils |
| Occupational acne |
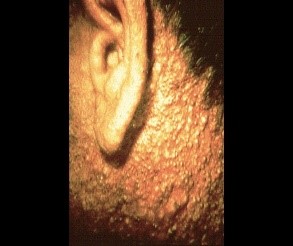
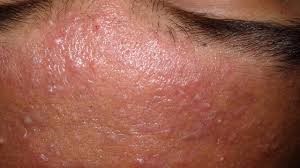
- Acne develops following exposure to certain agent at the workplace.
|
Oil, grease |
| Occupational leucoderma (vitiligo) |
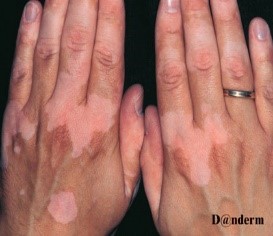
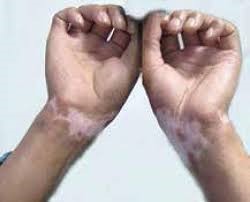
- White discolouration of the skin appears following exposure to certain agent at the workplace.
- Commonly at the areas of hands and forearms.
|
Phenols, hydroquinone,
dimethyl sulfate
|
Prevention:
How to prevent occupational skin disease?
- Avoid direct contact with hazardous agent which has been identified to cause skin disease to yourself.
- Practice personal cleanliness. Always wash exposed body parts (hands, face) following contact with hazardous chemical or agent at workplace.
- Use sunscreen for outdoor workers to protect from ultraviolet light
- Use of personal protective equipment to prevent direct contact with hazardous agent. Examples are gloves, face mask, long sleeve shirt, long pants and apron.
- Seek early medical advice if you think you have skin disease associated with work.
- Report to the employer about the disease so that suitable control measures can be taken to improve the working condition
Investigation:
How occupational skin disease is confirmed?
Disease normally improves with absence from work and recur on returning to work.
- Specific test such as a skin patch test and skin biopsy (part of the affected skin is taken for microscopic examination)
Treatment:
What is the treatment for occupational skin disease?
Treatment depends on:
- Type of skin disease
- Severity of disease
The most important measure to prevent recurrence of disease is to avoid further exposure to the hazardous agent, you might also be given certain medication to relieve the symptoms. In cancer cases, surgery to remove the skin cancer need to be done.
Notification:
According to Occupational Safety and Health (Notification of Accident, Dangerous Occurrence, Poisoning and Occupational Diseases) Regulation 2004, it is the responsibilities of :
- Employer
- Attending medical practitioner
To notify occupational diseases to Department of Occupational Safety and Health.
prepared by:
Dr. Siti Noor Azlidah Ali
Occupational Health Doctor (OHD)
Date of Input: 09/07/2019 | Updated: 09/07/2019 | izzatussofia
MEDIA SHARING