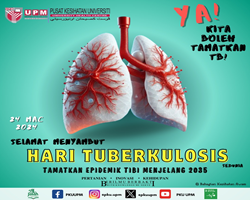
What is mumps?
Mumps is an illness caused by a virus. It typically causes painful swelling of the parotid glands (salivary glands located below the ear at the angle of the jaw). It is highly contagious and the virus spreads by droplets from the mouth, nose or throat when an infected person coughs or sneezes. It is most contagious three days before to four days after the onset of swelling.
What are its signs and symptoms?
It takes between 12 – 25 days after contact with an infected person for symptoms to start.
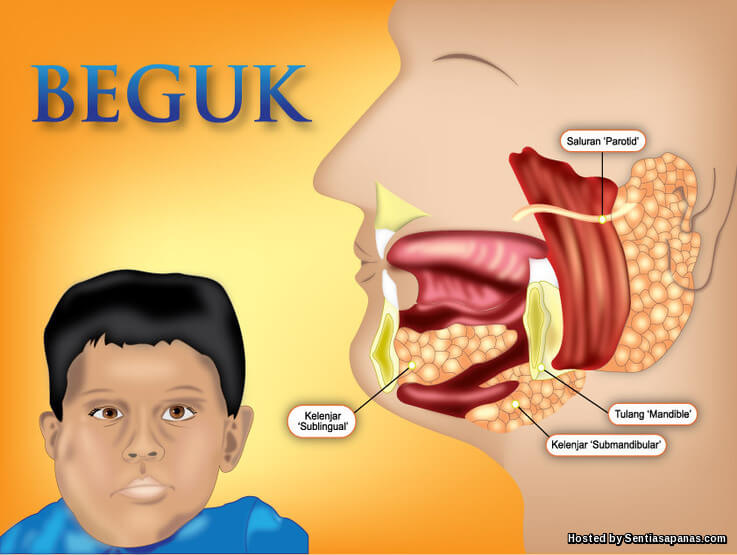
Some people with mumps have no symptoms, others may experience :
Fever
Headache
Dry mouth, loss of appetite
Pain upon opening mouth or eating
Tiredness
Swelling of one or both parotid glands which are situated at the angle of the jaw.
Symptoms usually resolve in 10 – 12 days.
Is it always a mild disease?
Although most people recover fully, rare complications may occur, these include :
Encephalitis (inflammation of the brain)
Meningitis (inflammation of the lining of the brain)
Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas)
Orchitis (inflammation of the testis) in adolescent or adult males
Deafness
How is mumps treated?
There is no specific treatment for mumps. The symptoms may be relieved by :
Paracetamol to bring down the fever and pain
Taking extra fluids but avoid acidic juices
Warm or cool packs at the parotid glands or testis to soothe the pain
An infected person should stay at home until no longer contagious (up to nine days after salivary gland swelling), or until the swelling disappears.
Can mumps be prevented?
Mumps can be prevented by vaccination. Mumps vaccine, given at 12 months and later at seven years old, as part of the MMR (Mumps, Measles and Rubella) vaccine, can effectively prevent mumps.
Date of Input: 13/07/2018 | Updated: 27/09/2018 | izzatussofia
MEDIA SHARING